What is the key difference between SLR and DSLR cameras?
In the world of cameras, DSLR cameras reign supreme in popularity. But what does DSLR actually mean? Well, DSLR stands for Digital Single Lens Reflex. Let’s break it down:
- “Digital” means it captures images digitally instead of using film.
- “Single Lens” indicates that the camera uses one lens for both capturing the image and viewing through the viewfinder.
- “Reflex” refers to how light is directed to the viewfinder through a mirror mechanism.
Here’s how it works: When you look through the viewfinder of a DSLR camera, you’re seeing exactly what the lens sees, thanks to a mirror inside the camera. This allows for precise framing and composition. When you press the shutter button, the mirror flips up, allowing light to hit the camera’s sensor, which captures the image digitally. So, a DSLR camera combines the convenience of digital photography with the familiarity and control of traditional single-lens reflex cameras.
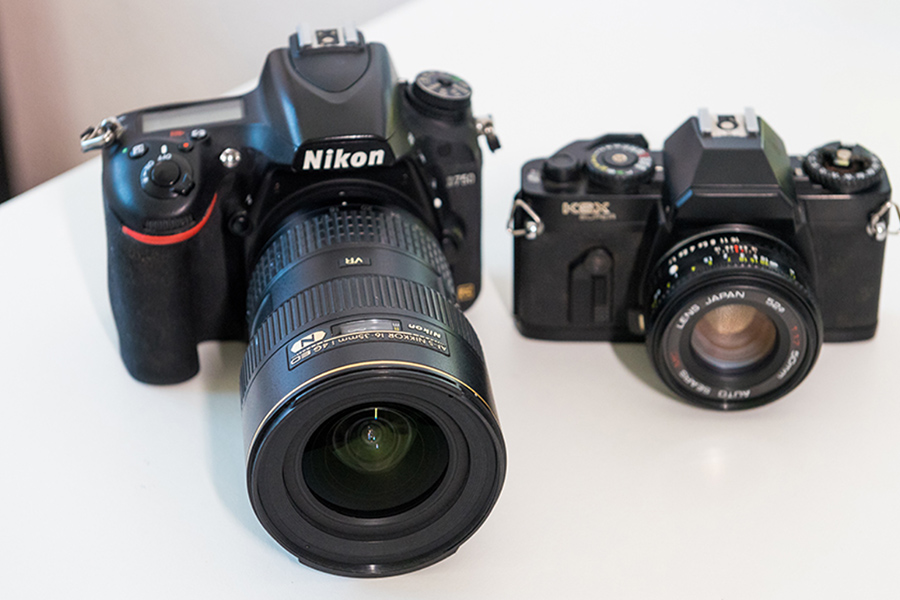

What is the key component of a DSLR camera?
The key component of a DSLR camera is its mirror, which plays an important role in creating and composing a photo. This mirror sits before the camera’s sensor and flips up when you press the shutter button to capture an image. When this happens, you’ll often hear a distinctive sound, like a quick slap. During this process, the viewfinder briefly goes dark because the mirror is momentarily blocking the light.
One major advantage of DSLR cameras is that you can see the scene or composition you photograph in real-time through the optical viewfinder. This isn’t possible with mirrorless cameras or smartphone cameras, which lack the mirror mechanism.

Another important component of a DSLR camera is its image sensor, often referred to as the camera sensor. This sensor’s size, measured in millimeters, plays a significant role in determining image quality, noise levels, and performance in low-light conditions.

Major camera manufacturers like Nikon, Canon, Sony, Pentax, and Fujifilm use two main types of sensors: CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) and CCD (Charged Coupled Device). These sensors come in different sizes, with the two main categories being full-frame and APS-C.
- Full-frame camera sensors, with dimensions around 35×24 millimeters, resemble the classic 35mm film size. This is why they’re called “full-frame.”
- APS-C sensors are slightly smaller, resulting in a crop factor that affects the angle of view compared to full-frame sensors.
Understanding the camera sensor size is essential as it greatly influences the overall performance and capabilities of the camera, particularly in capturing detailed images and handling challenging lighting conditions.

The APS-C (Advanced Photo System – Classic) camera sensor measures about 28.7 by 19 millimeters, making it smaller than a full-frame sensor. When using a DSLR camera with an APS-C sensor, the image appears cropped compared to what you’d see with a full-frame sensor. This cropping effect is often referred to as the crop factor.
This crop factor also affects the effective focal length of lenses. For instance, if the crop factor is 1.5x, a 50mm lens on an APS-C camera will provide a field of view similar to that of a 75mm lens on a full-frame camera. While this can be advantageous when using telephoto lenses, it can lead to limitations with wide-angle lenses.
Using the same wide-angle lens on both full-frame and APS-C cameras will result in a narrower field of view on the APS-C camera due to the crop factor. In simple terms, you won’t be able to capture the same wide scene with an APS-C sensor as you would with a full-frame sensor using the same lens.

Many DSLR camera manufacturers offer lenses designed for both full-frame and APS-C models. While it’s possible to use full-frame lenses on cameras with APS-C sensors, the reverse is not recommended.
For example, it’s physically impossible to use APS-C lenses on full-frame cameras with Canon cameras and lenses. This limitation underscores the importance of matching lens types to the camera’s sensor size for optimal performance and compatibility.
It’s important to understand that in DSLR cameras, the size of the image sensor (matrix) matters more for photo quality than the number of megapixels. Specifically, it’s about having the right balance of megapixels relative to the sensor size. When purchasing a DSLR camera, it’s important to consider all its features and understand how you’ll be using the photos.
Additionally, DSLR cameras typically feature multiple ports on their bodies for connecting various accessories such as adapters, external flashes, monitors, and microphones. These ports provide flexibility and versatility, allowing photographers to expand their creative capabilities and adapt to different shooting situations.

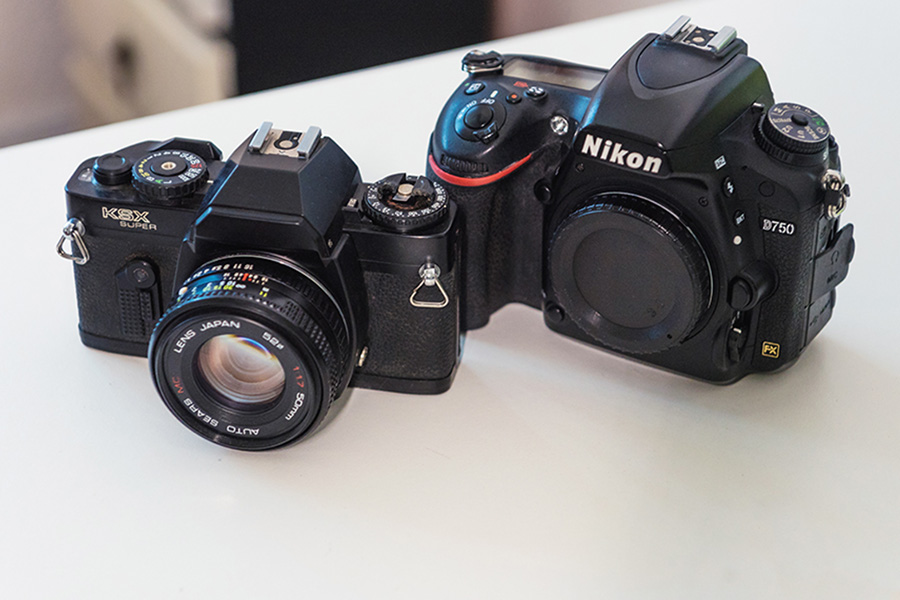
What is the difference between SLR and DSLR cameras?
The main distinction between a DSLR (Digital Single Lens Reflex) camera and an SLR (Single Lens Reflex) camera is the use of a digital sensor in the former and photographic film in the latter. The “D” in DSLR signifies the digital nature of the sensor, reflecting modern technological advancements.
Apart from the sensor, DSLR cameras feature a powerful image processing system, which occupies considerable space within the camera body. This system also accommodates an LCD screen. With the capability to record video and capture photos, most modern DSLR cameras come equipped with a built-in microphone and speaker. These additional features require a larger battery capacity in DSLR cameras than SLR cameras, ensuring sufficient power to support the extended functionality.
DSLRs enable storing thousands of photos on a memory card, whereas an SLR’s film roll holds around 36 images.
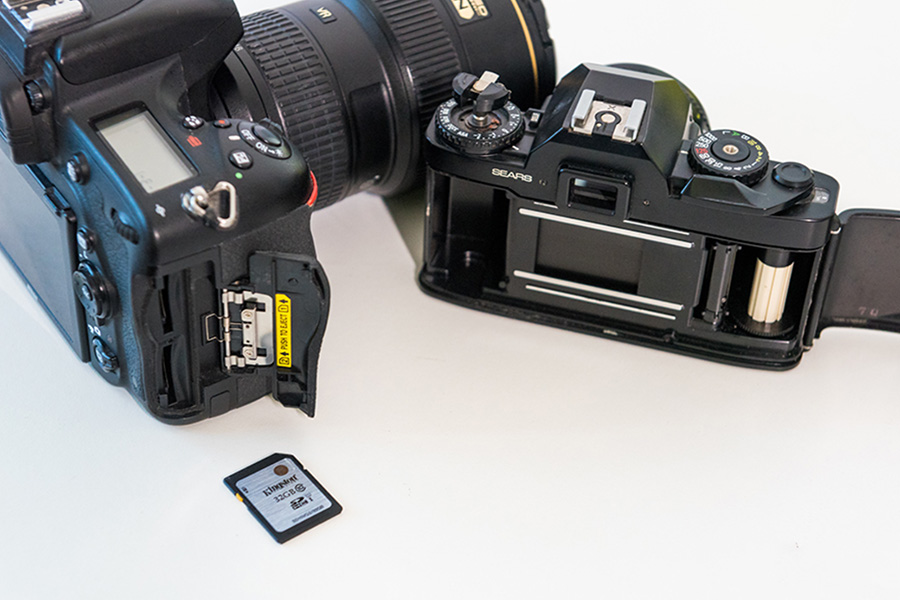

DSLR vs SLR
When comparing DSLR and SLR cameras, their basic operational principle remains the same: using the viewfinder to compose the scene, lifting the mirror, and releasing the shutter.
However, while it may be challenging to distinguish between a DSLR and an SLR camera at first glance, closer inspection reveals the differences. The key distinction lies in the presence of digital features. Upon closer examination, it becomes evident which camera is digital.
Best DSLR cameras in 2024
- Canon EOS Rebel T7
- Nikon D850
- Nikon D7500
- Canon EOS 5D Mark IV
- Canon EOS 90D
- Nikon D7500
- Canon EOS Rebel SL3
- Canon EOS Rebel T100
- Canon EOS-1D X Mark II
- Pentax K-1 Mark II
- Sony α7 IV
- Sony ZV-E10
- Pentax KF DSLRPentax K-1 Mark II
Stay inspired,
Elena Sullivan
Discover the perfect tool to start your photography journey! My beginner-friendly glossary is tailored just for you, packed with essential terms to simplify your learning process. Whether you’re just starting or looking to brush up on the basics, this glossary has everything you need to dive into the world of photography with confidence.

Sharing is caring
Elena
Hi, there! I'm Elena Sullivan! The founder of the ArsVie photo studio, trilingual photographer, online educator, woman in business cheerleader. Capturing life's moments with authenticity and elegance to inspire others. Passionate about helping businesses convey their message through compelling imagery.